The two major challenges of fermentation intelligence are data barriers and talent shortage!
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 18,2024
Summary
First of all, the conclusion is that intelligent fermentation is an inevitable trend in the future

Firstly, the conclusion is that intelligent fermentation is an inevitable trend in the future, and the main problems currently faced are severe data barriers and a shortage of cross disciplinary talents.
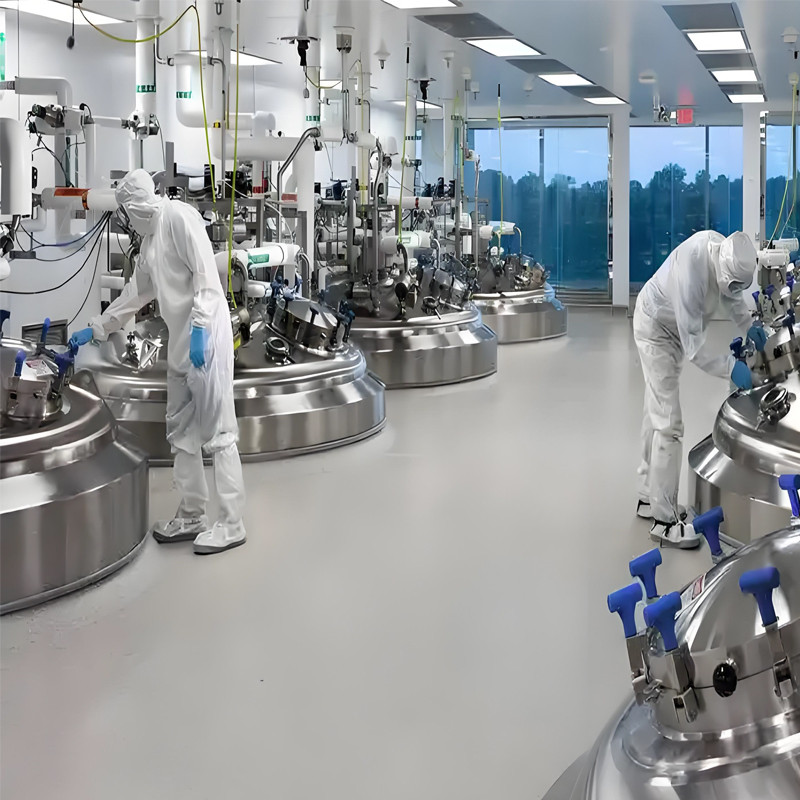
Fermentation intelligence is rapidly developing and maturing
Progress in sensor and data acquisition technology: A large number of high-precision and high-sensitivity sensors have been applied to the fermentation process, which can monitor key parameters such as temperature, pH value, dissolved oxygen, pressure, and flow rate in real time, and accurately transmit data to the control system.
Improved automation control level: Based on advanced control algorithms and automation equipment, the automation level of the fermentation process has significantly increased.
By using algorithms such as PID control, fuzzy control, and neural network control, precise control of fermentation parameters can be achieved, reducing manual intervention and improving the stability and repeatability of fermentation.
Enhanced data analysis and processing capabilities: By leveraging big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning technologies, we can deeply mine and analyze massive fermentation data, establish mathematical models for the fermentation process, and achieve real-time evaluation, fault diagnosis, and predictive optimization of fermentation status.
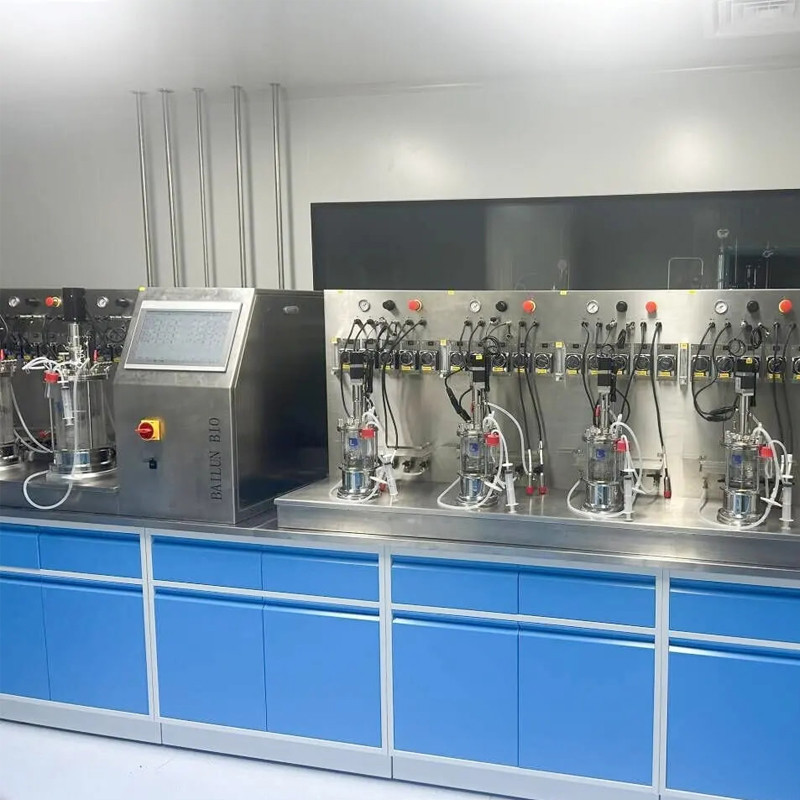

The application field of intelligent fermentation is broad
In the field of biopharmaceuticals, intelligent fermentation technology can ensure the stability and consistency of product quality, improve production efficiency, and reduce production costs in the production of antibiotics, vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and other biopharmaceuticals.
For example, by optimizing fermentation conditions, the yield and activity of drugs can be significantly improved.
Food and beverage industry: In the production of beer, Baijiu, yogurt, soy sauce and other traditional fermented foods, intelligent fermentation technology has been widely used.
For example, in the production of Baijiu, the intelligent control system is used to achieve precise control of fermentation temperature, humidity and other parameters, and improve the quality and taste of liquor.
In the field of bioenergy: In the production process of bioenergy represented by bioethanol, biodiesel, etc., intelligent fermentation helps to improve the utilization rate of raw materials and energy conversion efficiency, reduce production costs, and promote the development of the bioenergy industry.
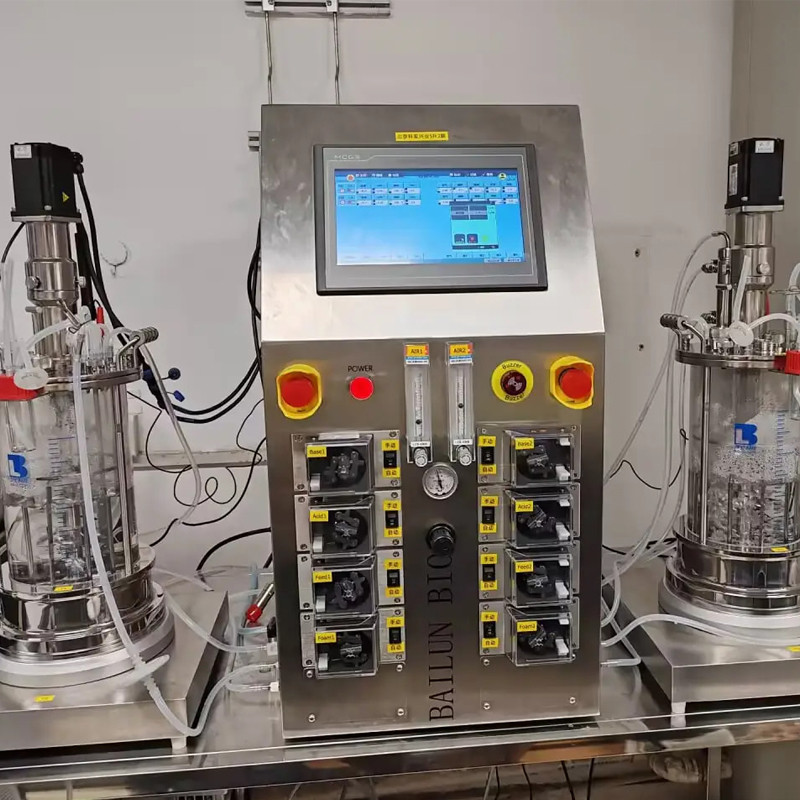

The challenges of intelligent fermentation mainly come from data and talent
Data, as a key element driving intelligence, is difficult to achieve effective integration and sharing due to the closed data between enterprises and research institutions.
The data formats and standards vary from different sources, and there are concerns about data security and privacy protection, making it difficult to build a comprehensive and accurate fermentation process big dataset.
This greatly limits the development and application of intelligent optimization algorithms based on big data analysis and machine learning, and cannot fully tap into the potential value of data to promote deep innovation in fermentation processes.
At the same time, the urgent demand for cross disciplinary talents in the field of fermentation intelligence is difficult to meet.
This field requires practitioners to have a deep understanding of the complex principles, process flow, and microbial characteristics of biological fermentation, as well as proficiency in various knowledge and skills such as automation control technology, computer programming, data science, and artificial intelligence algorithms.
However, the current education system and talent cultivation model are difficult to quickly adapt to this complex demand, resulting in a scarcity of professional talents who understand both biology and intelligent technology.
When enterprises promote fermentation intelligence projects, they often face the dilemma of no one available or existing personnel with a single knowledge structure that is difficult to handle the work, which seriously hinders the efficient development of fermentation intelligence technology research and development, system integration, and practical applications, and restricts the rapid development and upgrading pace of the entire fermentation intelligence industry.