Experience in Escherichia coli fermentation
- Share
- Issue Time
- Jan 1,2025
Summary
Experience and Influence of Escherichia coli Fermentation Process

Firstly, the feed rate and specific growth rate directly affect the production rate and accumulation of acetic acid (mainly because the feed rate and specific growth rate affect the residual sugar content in the fermentation broth, thereby affecting it). Therefore, controlling the feed rate and specific growth rate appropriately has a good effect on controlling acetic acid.
Secondly, sufficient dissolved oxygen should be ensured, the pH value should be strictly controlled, and the speed of acid and alkali supplementation should be moderate and not too fast; Temperature also has a significant impact on protein expression.
Most proteins produced by low-temperature fermentation are active, while proteins produced by high-temperature fermentation mostly exist in the form of inclusion bodies.
Thirdly, choosing a reasonable induction time is very important. Generally, the induction time is chosen in the later stage of exponential growth, and it is better to control the growth rate within 0.2 during induction.
At this point, induction: Separate the rapid growth phase from the protein synthesis phase, and ensure that the two phases do not affect each other, which is beneficial for high protein expression; Obtained a large number of bacterial cells, and the biomass of the bacterial cells is basically stable, which is reasonable from the perspectives of kinetics, energy consumption, and material cost.

Fourthly, the carbon nitrogen ratio during the feeding process is also important. Excessive nitrogen source leads to vigorous bacterial growth and high pH value, which is not conducive to the accumulation of metabolites.
If the nitrogen source is insufficient, the proliferation of bacterial cells will be reduced, which will affect the yield. If there is too much carbon source, it is easy to form a low pH and inhibit the growth of bacterial cells.
If the carbon source is insufficient, it is easy to cause bacterial aging and autolysis. In addition, improper carbon nitrogen ratio can also cause an imbalance in the proportion of nutrients absorbed by bacteria, directly affecting their growth and product synthesis.
Based on experience, in general, for a stable fermentation process, if there is always a phenomenon of bacterial dissolution during a fixed fermentation period, the possibility of bacteriophages and bacteria can be ruled out, which may be caused by an unreasonable carbon nitrogen ratio. The carbon nitrogen ratio can be adjusted appropriately.

Control of metabolic byproduct - acetic acid
Acetic acid is a metabolic byproduct during the fermentation process of Escherichia coli, and there have been different opinions on what concentration of acetic acid can have inhibitory effects.
It is generally believed that under good gas conditions, a concentration of 5-10g/L acetic acid can have a significant inhibitory effect on lag period, maximum specific growth rate, bacterial concentration, and final protein yield.
When the concentration of acetic acid is greater than 10 or 20g/L, cell growth stops. When the concentration of acetic acid in the culture medium is greater than 12g/L, the expression of exogenous proteins is completely inhibited.
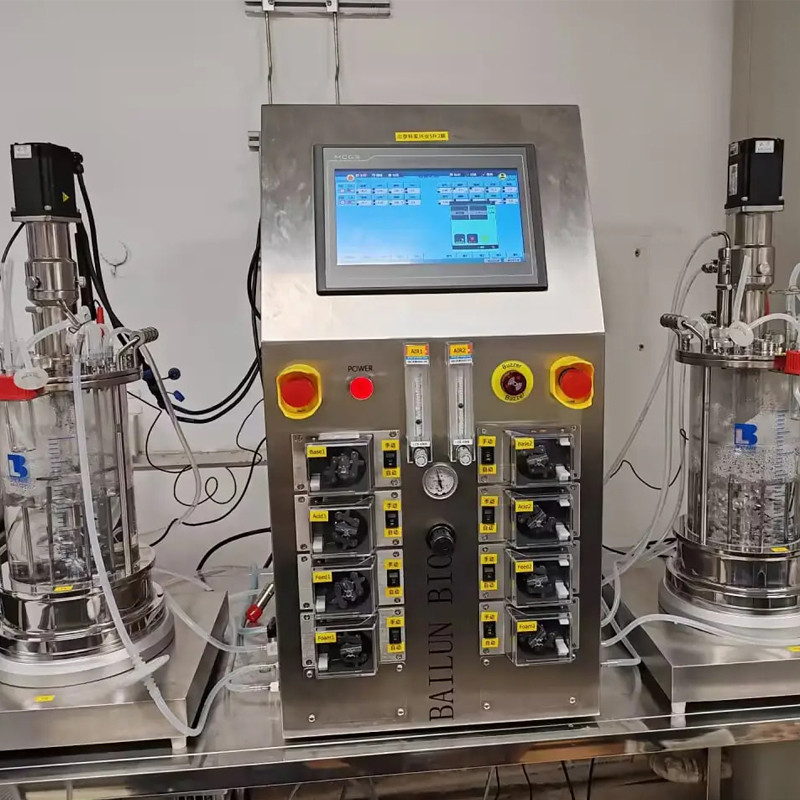

Measures to prevent the production of acetic acid
1. Reduce acetic acid production by controlling growth rate
The higher the specific growth rate, the more acetic acid is produced. When the specific growth rate exceeds a certain value, acetic acid will be produced. The growth rate can be reduced by lowering the temperature, adjusting the pH value, and controlling the feeding.
2. Dialysis cultivation
During the cultivation process of Escherichia coli, dialysis technology can be used to remove harmful substances from the fermentation broth, reduce the content of acetic acid, and achieve high-density fermentation and product expression of recombinant bacteria.
3. Control the concentration of glucose
Glucose is one of the important carbon sources in the fermentation process of Escherichia coli. The purpose of using glucose as a carbon source is to control it at a low level to reduce the production of acetic acid.

The commonly used control methods include constant pH method
Escherichia coli metabolizes grapes to produce acetic acid, which lowers the pH. Therefore, the pH value can be used as an indicator to control sugar content. The disadvantage of this method is that the change in pH value is not entirely the result of sugar metabolism, which can easily cause errors in the feeding system.
Constant dissolved oxygen method: The metabolism of bacteria consumes oxygen, reducing the amount of dissolved oxygen.
When the glucose concentration drops to a certain level, the metabolism of bacteria will decrease, oxygen consumption will decrease, and dissolved oxygen will increase.
Therefore, by adding glucose based on the dissolved oxygen curve and maintaining a constant dissolved oxygen, glucose can be controlled at a certain level.

The optimal temperature for fermentation of Escherichia coli is 37 degrees Celsius. When the temperature is most suitable for bacterial growth, the specific growth rate will increase.
As the temperature increases, the metabolism of bacteria accelerates, and the production of metabolic by-products also increases. These by-products can to some extent inhibit the growth of bacterial cells.
The stability of plasmids can also be affected by rapid bacterial growth. When the cultivation temperature decreases, the absorption of nutrients and the growth rate of bacteria will also decrease.
It can also reduce the production of toxic metabolic byproducts and metabolic heat. Sometimes lowering the temperature is more beneficial for the correct folding and expression of the target protein.
During the fermentation process of recombinant Escherichia coli, the optimal temperature varies at different stages of fermentation. To obtain a large amount of target protein, the first step is to ensure the quantity of bacterial cells.

Therefore, priority can be given to cultivating bacterial strains in the early stage and expressing the target product during the induction period.
The majority of E. coli fermentation uses batch feeding cultivation, which is a way to optimize modern fermentation processes and effectively optimize the chemical environment during microbial cultivation. Keep microorganisms in the optimal growth environment.
On the one hand, this method can avoid substrate inhibition when the initial concentration of certain nutrients is too high, and on the other hand, it can prevent the depletion of restrictive nutrients that affect cell growth and product formation.
Batch cultivation with supplementary materials has been widely used in the fermentation of various primary and secondary biological products and proteins.