Peptides are not only laboratory molecules, but also heavyweight drugs that can be produced on a large scale and distributed globally. Peptides stand at the golden intersection between small molecules and biomolecules
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 18,2025
Summary
Peptide drugs "is one of the fastest-growing and most innovative sub sectors in the field of biomedicine in recent years.


So, what are peptide drugs, why are they important, what challenges do they face, and where will they go in the future.
一、 What is a peptide drug? Peptides are chain like molecules composed of 2-50 amino acids connected by peptide bonds. When such molecules have clear pharmacological activity and can be used for disease treatment, they are called peptide drugs.
Typical representatives include: insulin (the world's first recombinant peptide drug, launched in 1982)
GLP-1 receptor agonist: Ozempic ®)、 Mounjaro peptide ®)—— The most popular weight loss/hypoglycemic drugs currently available include oxytocin, leuprorelin, teriparatide, etc
1、 Why are peptide drugs receiving increasing attention? 1. Precise targeting, small peptides with side effects can recognize "difficult to drug" targets such as G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and ion channels, with much higher selectivity than small molecules.
2. Significant therapeutic effect and high clinical value. Taking GLP-1 drugs as an example, they can not only lower blood sugar, but also reduce weight by 15% to 20%, and even lower cardiovascular risk - something that traditional drugs cannot achieve.
3. The R&D cycle is relatively short
Compared to monoclonal antibodies (5-10 years), peptide drugs typically take only 1-2 years from sequence design to preclinical candidates.
4. The explosive growth of the market has led to a global peptide drug market size exceeding 50 billion US dollars, with a compound annual growth rate of about 8%. Simaglutide alone will exceed $21.2 billion in sales in 2024, becoming the world's largest prescription drug.
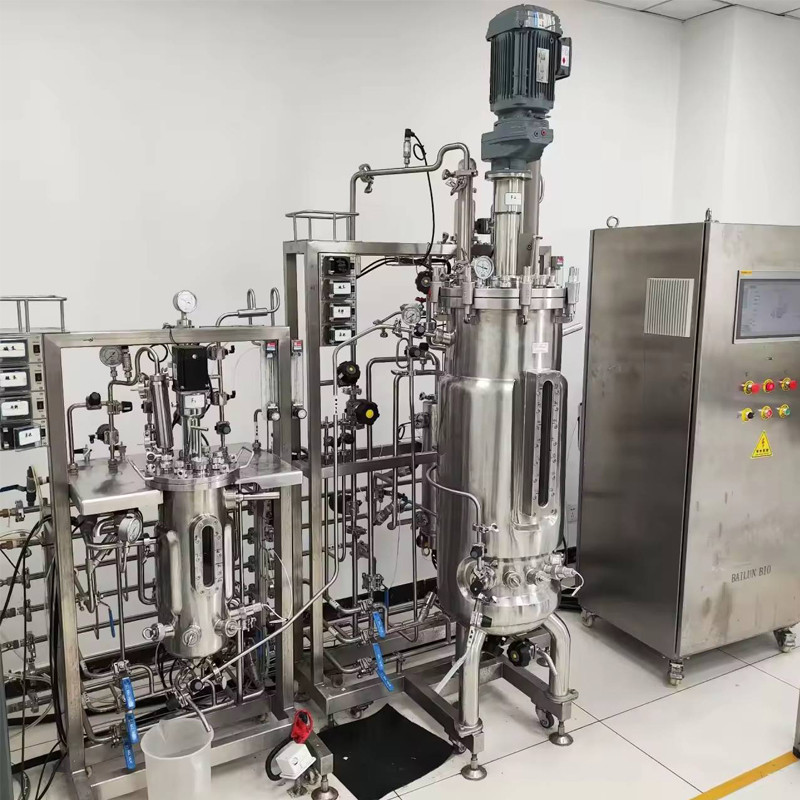

三、 But peptide drugs also have their 'hard wounds'
Challenge: Oral bioavailability is extremely low, and most require injection administration (subcutaneous/intravenous). Patient compliance is limited, and the half-life in the body is short and easily degraded by proteases. Frequent administration or structural modification is required, and the production process is complex.
Solid phase synthesis is costly, and the purification of long peptides is difficult. Quality control is strict, and patent barriers are high. Core sequences, modification technologies, and delivery systems are often monopolized by giants
Therefore, "long-term effect" and "oral administration" have become the two major directions for the industry to tackle.

四、 What are the future directions? Long term technology: fatty acid modification (such as semaglutide)
Oral peptide: Rybelsus oral semaglutide ®) Listed
Dual/multi-target peptide: Tirzepatide activates both GLP-1 and GIP receptors simultaneously, surpassing single target efficacy

五、 What does it mean for Chinese biopharmaceuticals? The GLP-1 boom has driven local enterprises to expand their presence (such as Xinda, Hengrui, Hanyu, Nuotai, etc.); The demand for peptide CDMO has surged (benefiting from companies such as WuXi AppTec, Kalein, and Sinovac Biotech).
There are also challenges: the core raw materials (Fmoc amino acids), high-end synthesis equipment, and delivery technology still rely on imports; Original targets and molecules are scarce.